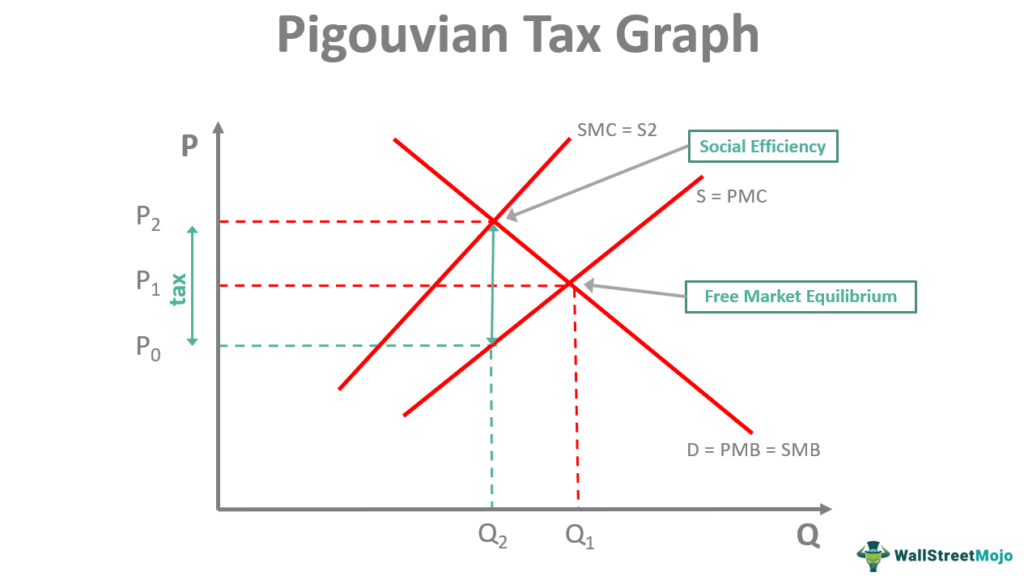
Pigouvian taxes are levies imposed on activities that generate negative externalities. These taxes aim to correct market inefficiencies and align private costs with social costs.
Want to test your knowledge? You can find A-Level Economics Past Paper Questions here.
Purpose
The main goal is to internalize externalities. By taxing the negative activity, the government encourages producers and consumers to reduce it.
Want notes on other topics? You can check out our Edexcel A-Level Economics Notes here.
Examples
- Carbon tax on emissions
- Sin taxes on alcohol and tobacco
Advantages
- Efficiency: Helps achieve social optimum.
- Revenue: Generates funds for the government.
Disadvantages
- Implementation: Difficult to set the correct tax rate.
- Equity: May disproportionately affect low-income groups.
Alternatives
- Subsidies for positive externalities
- Regulation and quotas
Real-world Applications
- Congestion charges in cities
- Plastic bag taxes
Criticisms
- May not fully correct the externality
- Potential for government misuse of funds

Mark is an A-Level Economics tutor who has been teaching for 6 years. He holds a masters degree with distinction from the London School of Economics and an undergraduate degree from the University of Edinburgh.